When we think of monkeys, one of the first images that often comes to mind is that of these playful primates swinging from trees while munching on bananas. This association has been deeply ingrained in popular culture and reflects a broader narrative that combines biology, ecology, and even mythology. In this article, we’ll delve into the captivating relationship between banana:b4hnuk08dew= monkey, exploring their biological ties, cultural representations, and the science behind their shared image.
The Biological Connection
1. Understanding Monkeys and Their Diets
Monkeys are part of the primate family and are primarily found in tropical and subtropical regions. They are divided into two main groups: Old World monkeys, which are native to Africa and Asia, and New World monkeys, found in the Americas. Both groups share certain characteristics but have distinct differences in their biology and behavior.
Old World Monkeys
Old World monkeys belong to the family Cercopithecidae and are characterized by their downward-facing nostrils and non-prehensile tails. Some well-known Old World monkeys include:
- Baboons: Known for their strong social structures, they live in troops and exhibit complex behaviors.
- Macaques: Highly adaptable, they can thrive in various environments, from forests to urban areas.
- Colobus Monkeys: These monkeys are known for their striking black-and-white fur and are primarily leaf-eaters.
Old World monkeys primarily consume fruits, leaves, seeds, and insects. banana:b4hnuk08dew= monkey, while not a staple in their diet, are often found in their natural habitats and are eagerly consumed when available.
New World Monkeys
New World monkeys belong to the family Platyrrhini and have flatter noses and prehensile tails, allowing them to grasp and hold objects. Some notable New World monkeys include:
- Capuchin Monkeys: Known for their intelligence, they often use tools and are popular in popular culture.
- Howler Monkeys: Famous for their loud howls, they primarily eat fruits and leaves, including bananas.
- Spider Monkeys: Agile climbers, they have long limbs and prehensile tails, making them adept at foraging in treetops.
New World monkeys also enjoy a varied diet, including fruits like banana:b4hnuk08dew= monkey, which provide essential nutrients and energy.
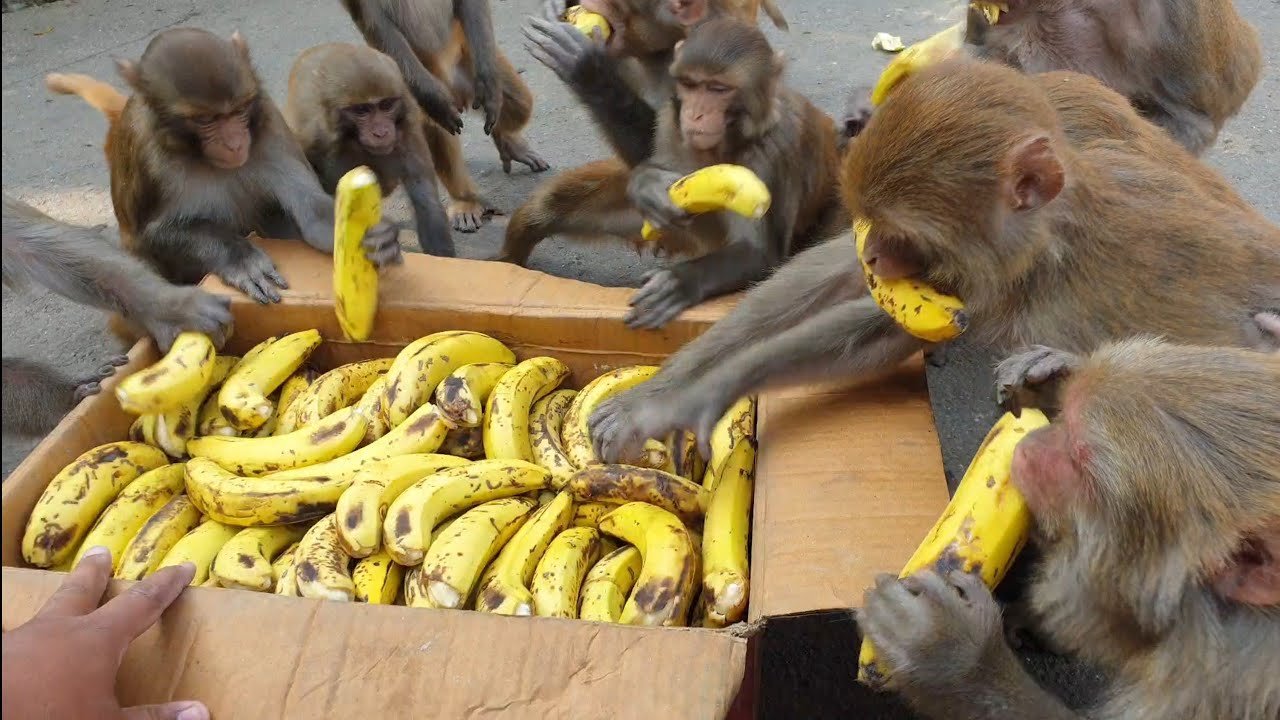
2. The Nutritional Value of Bananas
Banana:b4hnuk08dew= monkey are not only delicious but also packed with nutrients. They are rich in:

- Potassium: Essential for maintaining proper heart and muscle function. Potassium helps regulate blood pressure and supports overall cardiovascular health.
- Vitamin C: An antioxidant that helps boost the immune system and aids in the absorption of iron.
- Vitamin B6: Important for brain health and metabolism, Vitamin B6 plays a role in converting food into energy and is essential for the development of neurotransmitters.
- Dietary Fiber: Aids in digestion and promotes gut health. Fiber helps regulate bowel movements and can reduce the risk of gastrointestinal disorders.
For monkeys, bananas offer a quick source of energy due to their natural sugars, primarily glucose, fructose, and sucrose. The fruit’s soft texture makes it easy for monkeys to consume, allowing them to get the nutrients they need while foraging in their habitats.
3. Habitat and Foraging Behavior
Monkeys are often found in areas where bananas grow naturally. Many species inhabit tropical rainforests, which provide a rich variety of flora and fauna. The ability to climb trees enables monkeys to reach high-hanging fruits like bananas, which are often found in clusters.
In the wild, banana:b4hnuk08dew= monkey will use their intelligence and social structures to forage for food. They often work in groups, communicating and coordinating to gather the best food sources. This behavior demonstrates not only their adaptability but also their reliance on fruits like bananas for sustenance.
4. The Role of Bananas in Monkey Social Structures
Social structures within monkey troops can significantly influence foraging behavior. In many species, dominant individuals will have first access to food sources, including bananas. This hierarchical system affects how resources are shared within the troop.
Research has shown that social interactions play a vital role in how monkeys choose food. For instance, younger or subordinate monkeys may watch older individuals to learn which food sources are safe and nutritious. This learning process underscores the importance of social bonds in foraging success.
Additionally, some species of monkeys have been observed engaging in cooperative foraging, where they work together to access hard-to-reach food. This collaboration can lead to a more efficient gathering of bananas and other fruits, enhancing their chances of survival.
Cultural Significance of Bananas and Monkeys
1. Banana:b4hnuk08dew= Monkey in Popular Culture
The image of monkeys eating bananas has been a staple in cartoons, movies, and literature for decades. From the iconic cartoon character King Kong, who famously climbs the Empire State Building while holding a banana, to the animated series featuring playful monkeys, bananas have become synonymous with the portrayal of these lively creatures.
In children’s literature, banana:b4hnuk08dew= monkey are often depicted as mischievous characters who love bananas, reinforcing the connection between the two. Books such as “Curious George” have contributed to this narrative, featuring the inquisitive monkey engaging in various adventures, often involving bananas. The storylines typically highlight the playful nature of monkeys, allowing children to connect with these characters while exploring themes of curiosity and adventure.
Monkeys in Animation and Film
Animated films and shows have perpetuated the image of monkeys enjoying banana:b4hnuk08dew= monkey. For example:
- “The Jungle Book”: In this classic tale, the character King Louie, an orangutan, is portrayed as a fun-loving character who dances and sings about wanting to be human while indulging in bananas.
- “Madagascar”: The portrayal of the playful monkeys in this animated film showcases their antics, often revolving around food, particularly bananas, adding humor and entertainment.
These portrayals not only entertain but also contribute to the stereotypes surrounding monkeys and their fondness for bananas.
2. Monkeys in Mythology and Folklore
Across different cultures, monkeys have held various symbolic meanings. In some cultures, they are seen as tricksters, representing playfulness and mischief. The association with bananas amplifies this image, as the fruit is often portrayed as a source of joy and fun.
For example, in Hindu mythology, the monkey god Hanuman is revered for his strength and devotion. Although not directly linked to banana:b4hnuk08dew= monkey, the playful nature of monkeys in this mythology resonates with the cultural symbolism surrounding them. Hanuman is often depicted as a loyal companion, representing devotion and bravery, traits that are celebrated in stories across generations.
3. The Role of Monkeys in Ecological Balance
Monkeys play a crucial role in their ecosystems, particularly in tropical forests. As frugivores, they consume fruits like banana:b4hnuk08dew= monkey and help in seed dispersal. When monkeys eat bananas, they often travel some distance before excreting the seeds. This natural process contributes to the growth of new banana plants and other flora, promoting biodiversity and ecological balance.
This seed dispersal is vital for maintaining healthy ecosystems. By moving seeds away from the parent plant, monkeys help reduce competition for resources, allowing new plants to thrive in different locations. This behavior highlights the interconnectedness of various species and the importance of preserving habitats where monkeys and bananas coexist.
Bananas and Monkeys in Science and Research
1. The Study of Primate Behavior
Researchers have long studied monkeys to understand their behavior, social structures, and dietary preferences. Observing how monkeys interact with their environment and each other provides valuable insights into their biology and ecology.
Banana:b4hnuk08dew= monkey serve as a useful tool in these studies. They are often used as rewards in behavioral experiments, helping researchers understand learning processes, social dynamics, and foraging strategies. For instance, scientists may use bananas to test problem-solving skills, demonstrating how monkeys navigate challenges to obtain food.
Recent studies have focused on understanding the cognitive abilities of monkeys. Researchers have found that monkeys can plan for the future, using bananas as a motivator to engage in complex tasks. For example, studies have shown that monkeys can anticipate future needs and save bananas for later, showcasing their ability to think ahead.
2. Nutritional Studies
The nutritional value of bananas makes them an interesting subject for scientific research. Studies on the impact of dietary choices in primates can inform our understanding of human nutrition as well. Researchers often compare the dietary habits of monkeys with those of humans to explore the potential health benefits of various foods.
By studying how banana:b4hnuk08dew= monkey affect the health and behavior of monkeys, scientists can gather insights into the role of fruits in primate diets. These findings can be applied to improve human dietary practices and promote healthier eating habits. For example, research has demonstrated the importance of incorporating fruits like bananas into our diets for improved energy levels and overall health.
The Economic Impact of Bananas
1. The Banana Industry
The banana industry is one of the largest agricultural sectors globally, with countries like Ecuador, the Philippines, and Costa Rica being major exporters. Bananas are not only a staple food for humans but also play a significant role in the economies of these nations.
The cultivation of banana:b4hnuk08dew= monkey requires a considerable workforce, providing jobs for millions of people worldwide. In many tropical regions, banana plantations contribute to local economies, supporting families and communities. The banana industry also supports related sectors, such as transportation and distribution, creating a ripple effect throughout the economy.
2. Ecotourism and Monkey Watching
In areas where monkeys are native, ecotourism has become a significant industry. Tourists are drawn to locations where they can observe monkeys in their natural habitats. These tours often highlight the connection between monkeys and their food sources, including bananas.
Ecotourism promotes conservation efforts, raising awareness about the importance of preserving natural habitats. By providing economic incentives for conservation, communities can protect the environments that support both monkeys and the cultivation of banana:b4hnuk08dew= monkey. This symbiotic relationship benefits both local economies and the ecosystems in which these species thrive.
3. The Global Banana Market
The global demand for banana:b4hnuk08dew= monkey has led to significant advancements in agricultural practices. However, this demand also raises concerns about sustainability and environmental impact. The use of pesticides and monoculture farming can lead to soil degradation and loss of biodiversity.
Efforts are being made to promote sustainable banana farming practices that minimize environmental impact while ensuring fair labor conditions for workers. Certifications such as Fair Trade and Rainforest Alliance encourage sustainable practices and support local communities.
Fun Facts About Banana:b4hnuk08dew= Monkey
- Variety of Species: Over 260 species of monkeys exist worldwide, each with unique characteristics and diets, many of which include bananas.
- Intelligence: Monkeys are known for their intelligence and problem-solving abilities. Some species can use tools to obtain food, including bananas.
- Bananas Aren’t Just for Monkeys: While bananas are associated with monkeys, they are also enjoyed by many animals, including birds and insects, making them a vital food source in ecosystems.
- Cultural Representations: In addition to their portrayal in films and literature, bananas have been used in various art forms, symbolizing fertility, prosperity, and even humor in different cultures.
- Bananas and Health: Studies suggest that the high potassium content in bananas can help regulate blood pressure and reduce the risk of heart disease.

The Future of Bananas and Monkeys
1. Conservation Efforts
As the world faces environmental challenges such as deforestation, climate change, and habitat loss, the future of both banana:b4hnuk08dew= monkey and monkeys is at stake. Conservation efforts are crucial to protect the ecosystems that support these species.
Organizations dedicated to wildlife conservation are working to preserve monkey habitats, focusing on sustainable farming practices and responsible tourism. Educating communities about the importance of biodiversity and the role monkeys play in their ecosystems is essential for fostering a sense of stewardship.
2. Sustainable Farming Practices
Promoting sustainable farming practices in banana:b4hnuk08dew= monkey cultivation is critical to ensuring the long-term health of both the environment and local communities. Agroecological approaches, such as crop rotation, organic farming, and intercropping, can enhance soil health and reduce reliance on chemical inputs.
Sustainable practices not only benefit the environment but also improve the livelihoods of farmers by providing access to premium markets and increasing resilience to climate change. By adopting these methods, farmers can contribute to a more sustainable future for both bananas and the ecosystems in which they grow.
3. Education and Awareness
Raising awareness about the connections between banana:b4hnuk08dew= monkey, and the environment is essential for promoting conservation. Educational programs targeting schools, communities, and tourists can help foster a deeper understanding of the importance of protecting natural habitats.
Engaging storytelling through documentaries, social media campaigns, and interactive exhibits can capture the imagination and inspire action. By highlighting the intricate relationships between species and their environments, we can encourage collective efforts to safeguard our planet’s biodiversity.
Banana:b4hnuk08dew= Monkey: Conclusion
The relationship between banana:b4hnuk08dew= monkey is a captivating blend of biology, culture, and ecology. Bananas serve as an essential dietary component for many monkey species, while monkeys play a vital role in the growth and dispersal of these fruits. The cultural significance of this connection is reflected in popular media and mythology, reinforcing the playful and mischievous image of monkeys.
As we continue to explore the intricate relationships within our ecosystems, it’s essential to appreciate the interconnectedness of all living organisms. The bond between banana:b4hnuk08dew= monkey is just one example of how nature weaves together various threads to create a vibrant tapestry of life. By understanding and celebrating these connections, we can promote conservation efforts and ensure a balanced coexistence with the natural world.
Whether you’re a fan of these delightful primates or simply enjoy the sweet taste of banana:b4hnuk08dew= monkey, the fascinating connection between the two serves as a reminder of the beauty and complexity of our environment. As we look to the future, our commitment to protecting these species and their habitats will play a crucial role in sustaining the delicate balance of life on Earth.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ) About
Banana:b4hnuk08dew= Monkey:
Q1: Why are monkeys often depicted with banana:b4hnuk08dew= monkey?
A1: The association of monkeys with bananas stems from their natural diets in the wild. Monkeys are frugivores, meaning they primarily eat fruits, including bananas, which are commonly found in their habitats. This imagery has been reinforced through popular culture, cartoons, and literature, making it a recognizable stereotype.
Q2: Are bananas a significant part of a monkey’s diet?
A2: While bananas are not the primary food source for all monkey species, they do enjoy bananas when available. Monkeys consume a variety of fruits, leaves, seeds, and insects, with bananas being a valuable source of energy and nutrients like potassium and vitamin C.
Q3: How do monkeys find bananas in the wild?
A3: Monkeys utilize their keen senses and social structures to locate food. They are skilled foragers and often work in groups to identify fruit-bearing trees. Their ability to climb and navigate through the canopy allows them to access banana:b4hnuk08dew= monkey that grow high above the ground.
Q4: Do all species of monkeys eat bananas?
A4: Most monkey species will eat bananas if available, but dietary preferences can vary based on habitat and food availability. Old World and New World monkeys have different dietary habits, with some preferring leaves or flowers over fruits like bananas.
Q5: What role do monkeys play in the ecosystem regarding bananas?
A5: Monkeys are crucial for seed dispersal in their ecosystems. When they eat bananas, they help spread the seeds through their feces, contributing to the growth of new banana plants and promoting biodiversity within their habitats.
Q6: Can bananas be harmful to monkeys?
A6: Generally, bananas are safe for monkeys to consume. However, like any food, they should be part of a balanced diet. Overconsumption of sugary fruits like bananas can lead to health issues, so a varied diet is essential for their well-being.
Q7: How do cultural depictions of banana:b4hnuk08dew= monkey impact conservation efforts?
A7: Cultural representations of monkeys and their association with bananas can raise awareness about these animals and their habitats. However, stereotypes can also lead to misunderstandings about their behaviors and needs. Effective conservation efforts require accurate education and advocacy to promote the importance of preserving natural habitats.
Q8: Are there any health benefits to eating bananas for humans?
A8: Yes! Bananas are rich in potassium, vitamin C, vitamin B6, and dietary fiber. They can aid in digestion, support heart health, and provide a quick source of energy, making them a healthy snack option for humans.
Q9: What are the ecological impacts of banana:b4hnuk08dew= monkey cultivation?
A9: While banana cultivation is economically important, it can lead to environmental concerns such as deforestation, pesticide use, and loss of biodiversity. Sustainable farming practices are crucial to mitigate these impacts and protect ecosystems.
Q10: How can individuals contribute to the conservation of monkeys and their habitats?
A10: Individuals can contribute by supporting sustainable products, participating in ecotourism, and advocating for conservation policies. Educating themselves and others about the importance of preserving natural habitats can also make a significant difference in protecting these species.

Crafting Daily Lifestyle Narratives Across News and Business Horizons
Meet Joseph Tucker, a versatile blogger who navigates the intricate landscapes of lifestyle, news, business, and beyond. With a keen eye for detail and a passion for diverse niches, Joseph’s blogs are a testament to his ability to seamlessly blend lifestyle insights with the latest news and business trends. Whether offering practical lifestyle tips, dissecting current events, or unraveling the dynamics of the business world, Joseph’s writing invites readers to explore a rich tapestry of topics, where every blog post adds a new layer to our understanding of modern living. Mail: [email protected]